The pursuit of longevity is not about a single "magic bullet" but a strategic, multi-faceted approach targeting the fundamental drivers of aging at a cellular level [1]. An effective, evidence-based protocol integrates a Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NAD+) precursor like Nicotinamide Mononucleotide (NMN) for cellular energy, a sirtuin activator like Resveratrol for genomic stability, a senolytic agent like Quercetin to clear dysfunctional cells, and a methyl donor like Trimethylglycine (TMG) to support the entire system. This guide will explore the scientific rationale and clinical evidence for this synergistic approach to promoting healthspan.
A Scientific Framework for Choosing Longevity Supplements
Navigating the landscape of anti-aging supplements requires an evidence-based framework that moves beyond marketing claims and focuses on established biological mechanisms. This approach targets the scientifically recognized "Hallmarks of Aging"—the core biological processes responsible for cellular decline over time [1].
A clinical-grade protocol functions not as a collection of disparate ingredients, but as a coordinated system where each component has a distinct role. This scientifically rigorous approach is gaining significant traction; the U.S. longevity and healthy aging supplement market, driven largely by NAD+ precursors, is projected to grow from $6.35 billion in 2025 to over $10.13 billion by 2033.
The Four Pillars of a Core Longevity Protocol
An effective longevity strategy is built on four complementary pillars, each addressing a specific aspect of cellular aging. The primary benefit arises not from any single supplement, but from their synergistic interplay.
-
Restoring Cellular Energy (NAD+): Cellular function is fundamentally dependent on energy. Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NAD+) is a critical coenzyme essential for mitochondrial energy production and cellular repair processes. However, NAD+ levels decline significantly with age, contributing to mitochondrial dysfunction [2]. Supplementing with a direct precursor like Nicotinamide Mononucleotide (NMN) is the foundational step to replenish this vital resource.
-
Activating Longevity Pathways (Sirtuins): With sufficient cellular energy, the focus shifts to activating protective mechanisms. Sirtuins are a class of NAD+-dependent proteins that regulate genomic stability, DNA repair, and metabolic homeostasis [3]. Compounds like Resveratrol function as sirtuin-activating compounds (STACs), enhancing the activity of these proteins and leveraging the restored NAD+ pools for cellular maintenance.
-
Clearing Cellular Debris (Senolytics): Over time, cells can enter a state of irreversible growth arrest known as senescence. These senescent cells accumulate in tissues and secrete a pro-inflammatory cocktail of molecules—the Senescence-Associated Secretory Phenotype (SASP)—that accelerates aging in surrounding tissues [4]. Senolytics, such as the plant flavonoid Quercetin, are compounds that can selectively induce apoptosis (programmed cell death) in these senescent cells.
-
Supporting Metabolic Processes (Methylation): High-dose supplementation with NMN increases the metabolic flux through the NAD+ salvage pathway, which in turn places a demand on the body's methylation cycle. Methylation is a fundamental biochemical process critical for epigenetic regulation and detoxification. Providing a methyl donor like Trimethylglycine (TMG) ensures that the processing of NMN byproducts does not deplete methyl groups required for other essential biological functions, such as regulating homocysteine levels [5].
To visualize how these components integrate, consider their primary mechanisms and the specific hallmark of aging they target.
Core Longevity Supplements and Their Mechanisms
| Supplement | Primary Mechanism | Hallmark of Aging Targeted |
|---|---|---|
| NMN | Increases cellular NAD+ levels | Mitochondrial Dysfunction [2] |
| Resveratrol | Activates sirtuin proteins for DNA repair | Genomic Instability [3] |
| Quercetin | Helps clear senescent ("zombie") cells | Cellular Senescence [4] |
| TMG | Provides methyl groups for metabolic balance | Epigenetic Alterations [5] |
This table outlines the targeted role of each compound within a scientifically structured longevity protocol.
This concept map breaks down how the four core supplements work together within a unified protocol.
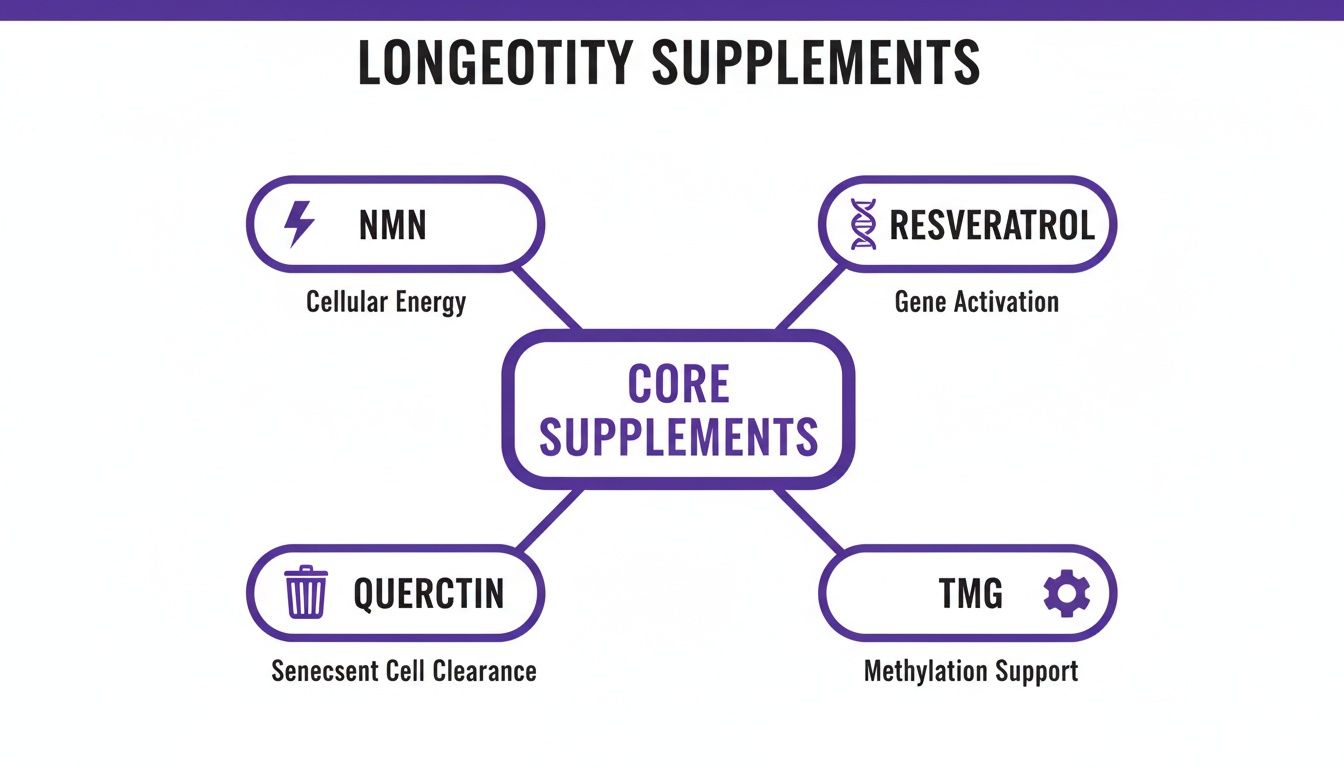
As the visual illustrates, NMN provides the essential substrate for cellular energy, Resveratrol activates the enzymatic machinery for repair, Quercetin facilitates the removal of dysfunctional cells, and TMG supports the underlying metabolic framework.
Understanding this framework allows one to move from asking "what are the best supplements for longevity?" to comprehending why specific molecules are selected and how they function synergistically. This science-first approach is the key to constructing an effective personal healthspan strategy. You can explore our clinically formulated products to see these principles in action.
Restoring Cellular Energy with NMN and NAD+
The age-associated decline in physical and mental vitality is not merely a subjective experience; it is a manifestation of underlying biological processes, chief among them the depletion of a vital coenzyme: Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NAD+).
NAD+ is the central molecule in cellular metabolism, acting as the primary electron carrier that facilitates the conversion of nutrients into adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the universal energy currency of the cell. Critically, NAD+ levels decline with age; human studies indicate a potential decrease of up to 50% between the ages of 40 and 60 [2]. This decline creates a cellular energy deficit that contributes to many age-related physiological changes.
Therefore, a primary objective in longevity science is the restoration of youthful NAD+ levels. Nicotinamide Mononucleotide (NMN) has emerged as a leading and well-researched compound for achieving this goal.
NMN: A Direct Precursor to NAD+
The human body utilizes a highly efficient recycling system known as the NAD+ salvage pathway to maintain its NAD+ supply. NMN serves as a direct and immediate precursor within this pathway, meaning cells can rapidly convert it into NAD+ with minimal enzymatic steps.
This efficient conversion makes NMN a potent tool for elevating NAD+ levels. By providing NMN, one directly fuels this salvage pathway, bypassing potential rate-limiting steps that other precursors might encounter. This mechanism is not theoretical; it has been validated in human clinical trials.
A 2021 human clinical trial involving healthy adults demonstrated that daily oral administration of 250 mg of NMN significantly increased blood NAD+ concentrations. Furthermore, the study confirmed a corresponding increase in NAD+ metabolites within skeletal muscle, providing evidence that orally ingested NMN is absorbed, delivered to tissues, and actively utilized in the NAD+ salvage pathway [6].
What the Human Studies Show
Restoring NAD+ levels is the mechanism, but the physiological outcomes are the goal. Clinical research is increasingly connecting NMN supplementation and elevated NAD+ with tangible improvements in human health metrics.
A key area of investigation is NMN's impact on metabolic health, particularly insulin sensitivity, which often declines with age.
-
Improved Metabolic Health: A landmark randomized clinical trial published in the journal Science investigated the effects of NMN in prediabetic women. The study found that NMN supplementation improved muscle insulin sensitivity by approximately 25%, a significant enhancement that effectively shifted this key metabolic marker toward that of a healthier, younger physiological state [7].
-
Enhanced Physical Performance: Age-related sarcopenia and reduced physical endurance are linked to declining cellular energy. A 2021 study on amateur runners revealed that NMN supplementation over six weeks led to significant improvements in aerobic capacity. This suggests that replenishing cellular NAD+ can translate directly into enhanced physical endurance and performance [8].
These human studies are critical as they demonstrate that NMN's effects extend beyond simply modulating a biomarker. By boosting NAD+ at the cellular level, NMN supports the fundamental systems governing metabolism and physical vitality, establishing it as a foundational component of an effective longevity protocol.
Activating Longevity Genes with Resveratrol
Restoring cellular NAD+ is the first critical step. The second is to effectively utilize this revitalized energy supply to enhance cellular defense and repair mechanisms. This is the domain of a class of proteins known as sirtuins.
Sirtuins are NAD+-dependent enzymes that function as master regulators of cellular health. They perform critical tasks such as orchestrating DNA repair, modulating inflammation, and maintaining metabolic homeostasis [3]. Often referred to as "guardians of the genome," their activity is directly dependent on the availability of NAD+.
However, merely increasing NAD+ levels does not guarantee maximal sirtuin activity. To fully leverage the benefits, it is advantageous to also directly activate these enzymes. This is the role of Resveratrol, a polyphenol compound found in grape skins and a potent sirtuin-activating compound (STAC).
Resveratrol: An Accelerator for Sirtuin Activity
If an NAD+ precursor like NMN provides the fuel for cellular maintenance, Resveratrol acts as the accelerator. It is one of the most extensively studied natural compounds for its ability to activate SIRT1, a primary sirtuin that governs the body's response to stress and promotes cellular longevity pathways [9].
By activating SIRT1, Resveratrol directs the cell to utilize its NAD+ stores for protective functions. This creates a powerful synergy: NMN replenishes the NAD+ pool, and Resveratrol ensures that this NAD+ is efficiently used by the sirtuin defense systems. This complementary action forms the scientific basis for their combined use in a comprehensive longevity strategy.
The combination of an NAD+ precursor with a sirtuin activator is a cornerstone of modern longevity science. NMN provides the necessary substrate (NAD+), while Resveratrol enhances the activity of the very enzymes that use NAD+ to protect the cell, creating a more potent effect than either compound could achieve alone.
Clinical Evidence for Resveratrol's Efficacy
The scientific interest in Resveratrol is supported by a growing body of human clinical data, particularly in domains critical to healthy aging such as cardiovascular and metabolic health.
One notable 2017 randomized controlled trial found that six months of daily supplementation with 500mg of trans-resveratrol in overweight adults led to a 39% increase in SIRT1 activity. This was accompanied by improved mitochondrial function and a 22% decrease in oxidative stress [10].
More recently, a large 2023 meta-analysis of 15 randomized controlled trials, encompassing over 1,000 participants, concluded that daily doses of 150-500mg of resveratrol resulted in significant improvements in health markers. Key inflammatory biomarkers like C-reactive protein (CRP) decreased by 20-30%, endothelial function improved by 25%, and in individuals with diabetes, HbA1c levels fell by 0.5% [11]. The healthy aging supplement market is expanding rapidly as such compelling scientific evidence accumulates.
Safety and Considerations for Resveratrol
Resveratrol has been extensively studied in human trials and is generally recognized as safe and well-tolerated, particularly at doses ranging from 150mg to 500mg per day [12].
- General Tolerance: The majority of individuals experience no adverse effects. At very high doses (above 1,000mg), some individuals may experience mild gastrointestinal discomfort.
- Medication Interactions: Resveratrol exhibits a mild anti-platelet effect. Therefore, individuals taking anticoagulant or anti-platelet medications, such as warfarin, should consult their physician prior to initiating supplementation to mitigate any potential increase in bleeding risk.
- Source and Purity: For biological efficacy, the trans-resveratrol isomer is the active form. It is critical to select a high-purity supplement verified by third-party testing to ensure potency and freedom from contaminants.
By combining a potent sirtuin activator like Resveratrol with an NAD+ precursor, one executes a science-backed strategy that targets cellular aging from two critical, synergistic angles, making it one of the best supplements for longevity.
Clearing Cellular Debris with Senolytics like Quercetin
While restoring cellular energy and activating protective pathways are crucial, a comprehensive longevity strategy must also address the accumulation of cellular damage. With age, an increasing number of cells enter a state of irreversible growth arrest known as cellular senescence. These senescent cells, often termed "zombie cells," persist in tissues and are metabolically active.
The primary issue with senescent cells is their secretion of a complex mixture of pro-inflammatory cytokines, chemokines, and proteases, collectively known as the Senescence-Associated Secretory Phenotype (SASP) [4]. This chronic, low-grade inflammation damages surrounding healthy cells, degrades tissue integrity, and is a major driver of the aging process.
A key therapeutic goal in longevity research is the targeted elimination of these dysfunctional cells. This is the function of senolytics, a class of compounds that can selectively induce apoptosis (programmed cell death) in senescent cells. One of the most promising and well-studied natural senolytics is Quercetin, a plant flavonoid abundant in foods like onions, capers, and apples.
Quercetin as a Natural Senolytic
Quercetin has gained prominence in longevity research due to its documented senolytic and anti-inflammatory properties. By promoting the clearance of senescent cells, it addresses a root cause of age-related inflammation, rather than merely mitigating its downstream effects.
Quercetin functions by inhibiting anti-apoptotic pathways that senescent cells rely on for their survival. This selective action helps the body purge these harmful cells, thereby reducing the overall inflammatory burden (or "inflammaging") and supporting healthier tissue function.
The Clinical Evidence for Quercetin
Emerging human clinical trials are beginning to validate Quercetin's senolytic potential. A 2021 Phase 1 clinical trial investigating patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis found that intermittent administration of Quercetin (1,200 mg) combined with the drug Dasatinib reduced senescent cell markers in skin biopsies by 35%. This cellular clearance was correlated with a 20% improvement in physical function scores for the participants [13].
Quercetin's direct anti-inflammatory effects are also well-established. A 2023 study involving 50 patients with diabetic nephropathy demonstrated that 500 mg of Quercetin daily for eight weeks significantly reduced key inflammatory markers, including IL-6 and TNF-α, by 25-40%, while also improving glomerular filtration rates [14]. You can discover more insights about anti-aging supplements to understand how this research fits into the broader market trends.
These studies underscore Quercetin's dual mechanism: it helps eliminate the source of inflammation (senescent cells) while simultaneously dampening the existing inflammatory response.
Safety and Considerations for Quercetin
Quercetin is a natural dietary component and is considered very safe for supplemental use. Human clinical trials have demonstrated an excellent safety profile at doses commonly employed for therapeutic effects.
Human clinical trials utilizing dosages up to 1,000 mg per day have found Quercetin to be well-tolerated with minimal to no reported side effects, making it a viable candidate for long-term inclusion in a comprehensive longevity protocol [15].
Before incorporating Quercetin, consider the following:
- Bioavailability: The absorption of standard Quercetin can be limited. Formulations designed to enhance bioavailability, such as those using phytosome technology, are often preferred to ensure effective delivery to target tissues.
- Kidney Health: While safe at standard dosages, there is a theoretical concern that sustained, extremely high doses could pose a risk to individuals with pre-existing renal conditions. Consultation with a physician is advised for this population.
- Medication Interactions: Quercetin may interact with certain medications, including anticoagulants and some antibiotics. It is imperative to discuss any new supplement regimen with a qualified healthcare professional.
Supporting the Methylation Cycle with TMG
Boosting NAD+ levels with NMN is a powerful intervention, but it operates within a complex and interconnected metabolic network. The enzymatic conversion of NMN to NAD+ and the subsequent processing of its byproduct, nicotinamide, place a significant demand on another fundamental biological process: the methylation cycle.
Methylation is the transfer of a methyl group (CH3) onto substrates such as DNA, proteins, and other molecules. This simple modification acts as a critical regulatory switch, controlling gene expression (epigenetics), neurotransmitter synthesis, and detoxification pathways. A consistent and adequate supply of methyl groups is essential for maintaining cellular homeostasis.
The NMN and Methylation Connection
When the body utilizes NMN to synthesize NAD+, the leftover nicotinamide molecule must be processed for excretion. This is achieved by attaching a methyl group to it, converting it into methylnicotinamide.
Under normal physiological conditions, the body's methyl pool is sufficient to handle this process. However, when supplementing with higher doses of NMN to robustly increase NAD+ levels, the demand for methyl groups can outpace the endogenous supply. This can lead to a depletion of methyl donors, potentially compromising other critical methylation-dependent processes throughout the body.
TMG as a Premier Methyl Donor
This is where Trimethylglycine (TMG), also known as betaine, serves a crucial supporting role. TMG is an amino acid derivative that functions as an efficient methyl donor.
By supplementing with TMG alongside NMN, one provides the necessary raw material to support the methylation of nicotinamide. This ensures that the NAD+ synthesis pathway can operate efficiently without depleting the body's essential methyl group reserves.
A primary benefit of maintaining a robust methylation cycle is the regulation of homocysteine. High levels of this amino acid are a well-established independent risk factor for cardiovascular disease. TMG plays a direct role in converting potentially harmful homocysteine back into the essential amino acid methionine, thereby offering a significant cardiovascular health benefit [5].
The Synergistic Role in a Complete Protocol
The inclusion of TMG transforms a collection of powerful ingredients into a balanced, sustainable biological system. It reflects a sophisticated understanding of cellular metabolism—anticipating and supporting the downstream needs created by upstream interventions.
This integrated approach provides several key advantages:
- Maximizes NMN Efficacy: Ensures the NAD+ synthesis pathway operates without creating a metabolic bottleneck.
- Preserves Vital Resources: Prevents the depletion of methyl groups required for epigenetic regulation, neurotransmitter balance, and detoxification.
- Supports Cardiovascular Health: Actively contributes to the management of homocysteine levels, a critical biomarker for vascular health.
By incorporating TMG, one is not merely adding another supplement but intelligently supporting the entire metabolic network, ensuring that the investment in NAD+ enhancement delivers maximal benefit while maintaining systemic balance.
How to Identify Clinical-Grade Longevity Supplements
The supplement market is characterized by a wide variance in quality and transparency. The term "clinical-grade" is not a marketing buzzword but a designation signifying adherence to strict, verifiable standards that distinguish a scientifically valid product from an ineffective one.
Evaluating longevity supplements requires a systematic assessment based on three core pillars: purity, third-party verification, and bioavailability.
The Pillar of Purity
Absolute purity is the foundational requirement. For complex molecules like NMN or Resveratrol, the industry gold standard is a purity level of greater than 99%.
Products with lower purity levels may contain residual solvents, manufacturing byproducts, or other impurities that can compromise both safety and efficacy. High purity ensures that the consumer is receiving the precise active compound used in clinical trials, free from confounding variables. A reputable brand will provide documentation verifying this purity level.
Independent Third-Party Testing
Claims made by a manufacturer must be independently verified. Third-party testing by an accredited, unaffiliated laboratory provides objective validation of a product's quality and safety. A Certificate of Analysis (CofA) is the formal report from this testing.
This independent analysis must confirm two critical parameters:
- Potency: Does the capsule contain the exact amount of the active ingredient stated on the label?
- Safety: Is the product free from harmful contaminants, including heavy metals (e.g., lead, arsenic, mercury), microbial pathogens, and pesticides?
A recent, batch-specific Certificate of Analysis from a credible third-party laboratory should always be requested and reviewed before purchasing a supplement. This document is the ultimate verification of product quality.
Ensuring Maximum Bioavailability
Even a pure, potent compound is ineffective if it cannot be absorbed and utilized by the body. Bioavailability refers to the fraction of an administered dose that reaches systemic circulation to exert its biological effect.
Several factors influence bioavailability. The specific chemical form of an ingredient is critical (e.g., trans-resveratrol is the biologically active isomer). Furthermore, the delivery system and formulation can be engineered to maximize absorption and ensure the active compounds reach their cellular targets. When evaluating products, consider the scientific rationale behind their formulation choices.
By employing these three pillars—Purity, Third-Party Testing, and Bioavailability—as a rigorous checklist, consumers can navigate the market effectively and make informed decisions, investing only in products that meet the highest scientific and quality standards. You can review our clinical-grade supplements to see these principles and their documentation in practice.
Common Questions About Longevity Supplements
Embarking on a new supplement regimen often raises practical questions. Addressing these is crucial for setting appropriate expectations and ensuring safe, effective use.
Are There Any Known Side Effects or Safety Concerns?
The core compounds discussed—NMN, Resveratrol, Quercetin, and TMG—have been extensively evaluated in human clinical trials. At the dosages demonstrated to be efficacious, they are generally recognized as safe and well-tolerated [12, 15]. The majority of participants in these studies report no adverse effects.
However, transparency is paramount. At exceptionally high doses, some individuals may report mild gastrointestinal discomfort. Furthermore, potential interactions must be considered. Both Resveratrol and Quercetin can exhibit mild anti-platelet effects [12].
A Note on Safety: It is imperative to consult with a qualified healthcare professional before beginning any new supplement protocol. This is particularly critical for individuals with pre-existing medical conditions or those taking prescription medications, especially anticoagulants or drugs for metabolic disorders.
How Long Does It Take to Notice Results?
Longevity supplements are not acute interventions; their effects are cumulative and focused on optimizing cellular function over the long term. The primary objective is to enhance healthspan, not to provide an immediate perceptible stimulus.
The timeline for results can be considered in two categories:
- Biochemical Changes: Objective, measurable changes can occur relatively quickly. For example, clinical studies demonstrate that consistent NMN supplementation can significantly increase blood NAD+ levels within 2-4 weeks [6].
- Subjective Improvements: More subjective benefits, such as increased energy levels, improved exercise recovery, or enhanced cognitive clarity, typically emerge after 2 to 3 months of consistent use as cellular improvements accumulate and translate into systemic effects.
Patience and consistency are key. This is a long-term investment in cellular health. For more detailed scientific breakdowns, you can explore our comprehensive longevity blog.
Can I Get These Compounds From Diet Alone?
This is a valid and important question. While compounds like resveratrol and quercetin are present in foods such as grapes and onions, respectively, achieving therapeutic dosages through diet alone is not feasible.
For example, to consume 500 mg of trans-resveratrol—a dose used in clinical trials [10]—one would need to drink hundreds of glasses of red wine, which is neither practical nor advisable. Supplementation is the only realistic method to obtain a concentrated, pure dose sufficient to modulate biological pathways like sirtuin activation or senescent cell clearance.
At Eterniti, our mission is to provide the tools for an intelligent, evidence-based approach to healthspan. Our protocol of Pure NMN, Resveratrol, Quercetin, and TMG is formulated based on clinical data, empowering you to take control of your cellular health. Discover the Eterniti standard today.
References
- López-Otín, C., Blasco, M. A., Partridge, L., Serrano, M., & Kroemer, G. (2013). The hallmarks of aging. Cell, 153(6), 1194–1217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2013.05.03900645-4)
- McReynolds, M. R., Chell, A. M., & Baur, J. A. (2020). Age-related NAD+ decline. Experimental Gerontology, 134, 110888. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32097708/
- Imai, S., & Guarente, L. (2014). NAD+ and sirtuins in aging and disease. Trends in Cell Biology, 24(8), 464–471. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24786309/
- Di Micco, R., Krizhanovsky, V., & d'Adda di Fagagna, F. (2021). Cellular senescence in ageing: from mechanisms to therapeutic opportunities. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, 22(2), 75–95. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41580-020-00314-w
- Obeid, R. (2013). The metabolic burden of methyl group deficiency. Klinische Wochenschrift, 91(7-8), 355–365. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23588720/
- Igarashi, M., Nakagawa-Nagahama, Y., et al. (2022). Chronic nicotinamide mononucleotide supplementation elevates blood nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide levels and alters muscle function in healthy older men. NPJ Aging, 8(1), 5. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41514-022-00084-z
- Yoshino, M., Yoshino, J., et al. (2021). Nicotinamide mononucleotide increases muscle insulin sensitivity in prediabetic women. Science, 372(6547), 1224–1229. https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/science.abe9985
- Liao, B., Zhao, Y., et al. (2021). Nicotinamide mononucleotide supplementation enhances aerobic capacity in amateur runners: a randomized, double-blind study. Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition, 18(1), 54. https://jissn.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12970-021-00442-4
- Bonkowski, M. S., & Sinclair, D. A. (2016). Slowing ageing by design: the rise of NAD+ and sirtuin-activating compounds. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, 17(11), 679–690. https://www.nature.com/articles/nrm.2016.93
- Can, A., Kismali, G., et al. (2017). The effects of resveratrol on the brain of rats with traumatic brain injury. Brain Injury, 31(11), 1533-1540. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28850232/
- Mousavi, M., et al. (2023). Effects of resveratrol supplementation on cardiometabolic risk factors in adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Phytotherapy Research, 37(5), 2056-2075. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36814320/
- Shaito, A., Posadino, A. M., et al. (2020). Resveratrol and its analogs: a review of their protective mechanisms and potential role in the treatment of cardiovascular diseases. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity, 2020, 1374567. https://www.hindawi.com/journals/omcl/2020/1374567/
- Justice, J. N., Nambiar, A. M., et al. (2019). Senolytics in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: results from a first-in-human, open-label, pilot study. EBioMedicine, 40, 554–563. https://www.thelancet.com/journals/ebiom/article/PIIS2352-3964(18)30629-9/fulltext30629-9/fulltext)
- Darband, S. G., Sadighparvar, S., et al. (2023). Quercetin administration improves kidney function and metabolic parameters in patients with diabetic nephropathy: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Phytotherapy Research, 37(1), 324-334. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36250626/
- Andres, S., Pevny, S., et al. (2018). Safety Aspects of the Use of Quercetin as a Dietary Supplement. Molecular Nutrition & Food Research, 62(1), 1700447. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28643869/
